|
MAIN PAGE
> Back to contents
Sociodynamics
Reference:
Karimov A.G., Kadyrov S.K., Svinukhova Y.N.
Resource capital of a modern family in the Republic of Bashkortostan: differentiation of opportunities and compensating factors
// Sociodynamics.
2023. № 12.
P. 103-117.
DOI: 10.25136/2409-7144.2023.12.69054 EDN: NMDBMY URL: https://en.nbpublish.com/library_read_article.php?id=69054
Resource capital of a modern family in the Republic of Bashkortostan: differentiation of opportunities and compensating factors
Karimov Aibulat Galim'yanovich
PhD in Sociology
Leading Researcher, Head of the Sector of Socio-Political Research, Institute of Socio-Economic Research - a separate structural unit of the Federal State Budgetary Scientific Institution of the Ufa Federal Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences
71 Oktyabrya Avenue, Ufa, Republic of Bashkortostan, 450054, Russia

|
karaigal@gmail.com
|
|
 |
Kadyrov Salavat Khismatovich
PhD in Economics
Senior Researcher, Institute of Socio-Economic Research - a separate structural unit of the Federal State Budgetary Scientific Institution of the Ufa Federal Research Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences
71 Oktyabrya Avenue, Ufa, Republic of Bashkortostan, 450054, Russia

|
P02_KadyrovSH@gks.ru
|
|
 |
|
Svinukhova Yuliya Nikolaevna
Scientific Associate Institute for Social and Economic Research of Ufa Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences
450000, Russia, Republic of Bashkortostan, Ufa, Prospekt Oktyabrya str., 71

|
s.ioulia@mail.ru
|
|
 |
Other publications by this author
|
|
|
DOI: 10.25136/2409-7144.2023.12.69054
EDN: NMDBMY
Received:
21-11-2023
Published:
31-12-2023
Abstract:
The object of the study is families living in the Republic of Bashkortostan. The subject of the study is the resource capital of a family with children. One of the important areas of research is the consideration of a family with children in the aspect of a resource approach. The relevance of the study is determined by the need to monitor and assess the needs and access to social benefits and services of families and their members, which will determine some mechanisms for improving their socio-economic status, respectively, well–being and quality of life, and will also determine the characteristics and degree of influence of various types of its capital in family education. The paper uses statistical data analysis, secondary analysis of sociological research data on related issues. The actual basis of the study was the data obtained during the study of the living conditions of the population in 2022 in the Republic of Bashkortostan conducted by the state statistics bodies. The paper considers the current socio-economic status of families living in the region. The factors causing the risk of reducing the well-being of families with children are identified, the directions of their impact are determined. Based on the data presented, it is shown that the risk of a decrease in the material well-being of families with children in the region is primarily caused by factors such as having many children and living in rural areas. The paper shows that the financial capital of families with children for a significant part of them acts rather as a factor limiting development opportunities and access to social goods and services. The social capital of families can act as a compensating factor and even expand life opportunities, in particular, in the field of education. Some mechanisms of leveling the factors that reduce the well-being of families with children are indicated.
Keywords:
family, socio-economic status, needs satisfaction, financial capital, social capital, quality of life, welfare, well-being, conversion of forms of capital, resource approach
This article is automatically translated.
You can find original text of the article here.
This study was carried out within the framework of the state assignment of the UFIC RAS No. 075-01134-23-00 for 2023 and for the planning period of 2024 and 2025. Introduction Against the background of the tense geopolitical situation in such a difficult period for Russia, more and more attention is being paid to the development of the family as a powerful framework for the progress of Russian society and a stronghold of traditional values [1]. The theoretical and methodological foundations of modern family research allow us to consider it not only as a basic institution of socialization, transmitting behavioral models and instilling values, norms of behavior and knowledge, which are the basis for the development of the younger generation. One of the important areas of research is the consideration of a family with children as an object of research in the aspect of a resource approach. The question of the role of the parental family, the importance of family resources and the possibilities of using their entire arsenal in the implementation of the life strategies of the younger generation can be considered, perhaps, already classic in sociological science. However, from the point of view of quality of life management in the region, the relevance of the study is determined by the need to monitor and assess the needs and access to social benefits and services of families and their members, which will determine some mechanisms for improving their socio-economic status, respectively, well–being and quality of life, and will also determine the characteristics and degree of influence of various the types of her capital in family education. Methods The study of a modern family with children presented in the work is based on a resource approach. The theoretical and methodological foundations of the study were the works of domestic researchers containing a sociological analysis of the structure and characteristics of the capital of the parent family depending on the social status of the family, an analysis of the influence of various components of family capital on the formation of youth. In Russian sociological science, a model of family capital has also been developed, including detailed structural operationalization of such elements as economic, cultural and human capital [2], which is of interest for highlighting areas of analysis of the resource capital of families with children in the region. In this paper, the family is analyzed as a conglomerate of material or financial, social, cultural and human capital, therefore it can be considered from the point of view of its tangible and intangible assets. At the same time, the family's resource capital – the level of provision of families with financial and social resources, acts as the main source of well-being of their members and a factor determining the capabilities and attitudes of children and adolescents in the areas of value and professional orientations, health, personal growth and education. It will either expand start-up opportunities, or act as a serious obstacle and limit access to basic social values, goods and services. An analysis of research in the field of the realization of the family's resource capital shows that not only material opportunities, but also the level of its socio-cultural capital affects, for example, access to education. Thus, by introducing the concept of family capital into Russian sociology, O.I. Shkaratan and G.A. Yastrebov consider it as the most important resource and factor of children's educational trajectories [3]. V.V. Fursova shows that the socio-cultural capital of the parent family is able to influence the choice of educational institution, profession, educational strategies, and therefore determines achievements, career and social status. And cultural deprivation and lack of social capital lead to unequal chances in educational achievements [4]. P. Bourdieu, a classic of the theory of social capital, also speaks about the differentiation of attitudes towards investments in the education of children among families from different social environments, the reason for this is not only the material capital of the family, but also "... the relative weight of cultural capital in the general culture of inheritance..." [5]. One of the most important points of the analysis is the emphasis on the property of converting various forms of family capital. This property is highlighted by V.V. Radaev, which he defines as the ability of one form of family capital to transform into another, to act as a source of accumulation of its other forms. Thus, economic (financial) capital expands educational opportunities, which, in turn, increases the volume of human capital. And the actual human and cultural capital can be the basis for obtaining a higher-paying job and, accordingly, help to increase income and status [6]. The income level of a family is an undoubted differentiating factor and determines the level of its ability to meet the basic needs of its members. It also differentiates value-normative attitudes and consumer behavior, causing conditions for unequal access to material, social and cultural benefits. For example, to the same education, which at the individual level is increasingly beginning to acquire value not only as symbolic capital, but also to become a way of life – an element of self-actualization and competitiveness. However, an analysis of the available publications on the research topic [2-10] allows us to conclude that the family as a social institution has some compensating resources or factors – cultural and social capital, which in some cases are able to cover the lack of material. The work uses statistical data analysis, secondary analysis of sociological research data on related issues. The actual basis of the study was made up of data obtained during a study of the living conditions of the population in 2022 in the Republic of Bashkortostan (RB) conducted by state statistical agencies [11]. Results
The factors of limitation and the directions of their impact. One of the main categories used to describe the economic and social living conditions of families is socio-economic status as a factor determining well-being and quality of life. Well-being and quality of life are multidimensional concepts, which also include a subjective attitude to living conditions. Having analyzed various models and methods of quality of life management [12-19], it can be concluded that its analysis regarding families with children in the region should be concentrated within its 5 main components. Namely: assessment of income level; assessment of the level of housing and household provision; assessment of the level of accessibility of medical services; assessment of the availability of education and additional services in this area; assessment of opportunities for full-fledged development. The level of income and deprivation. Let's consider the trends in the financial capabilities of families with children in the Republic of Belarus, formed on the basis of their monetary income. One of the most common research methods here is the measurement of subjective satisfaction and assessment of deprivation, i.e. the assessment of limitations in meeting basic human needs in housing, food, clothing, shoes, education, healthcare, etc. The results of surveys conducted by state statistical agencies in the Republic of Belarus showed that the assessment of their financial situation by respondents from families with children under the age of 18 does not look very favorable. An analysis of the quality of life of families with children through the prism of deprivation has shown that today families with children in the Republic of Belarus experience on average from 3 to 4 deprivations for basic life support needs. A significant part of families with children in the Republic of Belarus experience difficulties of a domestic nature and in the organization of recreation and recreation (49.1% of respondents indicated the inability to spend one week of vacation outside the home every year, 47.3% – are unable to replace furniture that has fallen into disrepair, 48.9% – are unable to cope with unforeseen expenses during housing repairs) [11]. It should be noted that the all-Russian trends have already become traditional, in which the share of poor families with three or more children significantly exceeds the share of those without children. In the Republic of Belarus, in families with children under the age of 18, the poverty rate in 2022 was 12.2%, while in childless families it was only 2%. The subjective perceptions of the surveyed households with children under the age of 14 also indicated rather a negative assessment of their financial situation. Thus, 81.4% of respondents indicated that they could "make ends meet" with difficulties to one degree or another. The problem point is often the payment of increased housing and communal services for households with children - 80.1% noted the presence of arrears on these payments by two or more times [11]. The problem of low-income families with several children is determined not only by low income. A significant factor is that the material resources available to the family should be distributed among the needs of a larger number of family members, i.e. there is a shortage of the family budget, which means that there is a feeling that there are not enough resources for existence. At the same time, with rising prices and an increase in the number of families, the share of food costs tends to increase. As a result, not only the volume and quality of services consumed to maintain the health, education and recreation of all family members suffer, but also the diet itself and the quality of nutrition. And this, in turn, poses a threat at the level of reproduction of human capital. Families falling into this category are forced to first provide their primary needs for food and housing, significantly reducing the cost of cultural goods, since their level of well-being does not allow them to acquire secondary values and services in the right amount compared to food [20]. The amount of monetary resources in families with several children almost always lags behind the average values, which is confirmed by the data shown in Figure 1. These data indicate that the risk of reducing the material well-being of families with children is caused by factors such as having many children and living in rural areas. 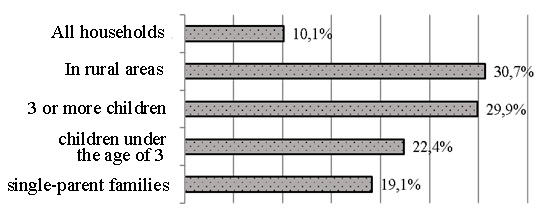 Figure 1. Households with children under the age of 18 with incomes below the subsistence minimum in the Republic of Belarus in 2022, % [11] The RB data correlate with trends in Russia. Studies conducted on the materials of Rosstat also show that the level of deprivation of households depends on the degree of urbanization of the settlement. Thus, the study of material deprivation of Russian households presented in [15] shows that the smaller the settlement, the more deprivation residents experience – on average up to 4-5 or more deprivations in rural settlements. There are more than a third of such households in rural areas. Consequently, the relationship between indicators of material deprivation and the place of residence is almost linear. It should be noted that the problem of poverty in the republic, as well as in Russia as a whole, lies primarily in rural poverty. If the poverty rate in urban areas was 2.3%, then in rural areas it was 15.9%. The share of rural residents was 80.6% of the total poor population, urban residents – 19.4% [11]. The main source of income for all families is income from work. At the same time, social transfers also act as one of the components of monetary incomes of families and an important means of equalizing the level of well-being. If we consider the structure of monetary incomes of families, we can conclude that by 2022 in the Republic of Belarus families with children received social support in the form of benefits and compensations in monetary terms, not much different from the average for households and even from childless families.
Obviously, raising social transfers to families with children to an average level does not allow them to be lifted out of poverty. The amount of monetary income that a household does not have enough to reach the subsistence level, according to the observation data, amounted to 2,478 rubles per household member in families with children. Thus, in order to lift families out of poverty, social benefits must be increased 2.1 times. The proportion of the poor living in households with children under the age of 18 was 87.6% of the total poor population. Therefore, it is extremely important to increase the targeting of social measures aimed at reducing poverty in the context of a decrease in real monetary incomes of the population [11]. Housing and household services. Studies on the problems of families with children show that there is a differentiation of the living conditions of families depending on the presence of children in them [21]. According to regional surveys conducted by state statistics agencies, families with children are in much worse housing conditions, almost one in ten families lives in a communal apartment or hostel. Only half of the respondents rate their housing as excellent and good. It should be emphasized that about 8% of citizens with children described their housing as bad and very bad. A serious problem for urban families with children is poor noise insulation (22.6%) and lack of heat (13.6%). In rural areas, excess humidity and dampness (12%) are of the greatest concern [11]. The data in table 1 clearly show diametrically opposed estimates of living conditions, especially among urban families with children. Thus, more than 40% of families with children felt the need to improve their living conditions, while such families without children were noticeably lower. Table 1 Assessment of living conditions and the condition of their homes among households in the Republic of Belarus in 2022, % [11] | Evaluation criteria | they live in urban settlements | they live in rural settlements | | d/x s children | d/x without children | d/x s children | d/x without children | | All households | 100,0 | 100,0 |
100,0 | 100,0 | | The housing conditions are generally satisfactory | 58,7 | 81,8 | 58,5 | 69,4 | | they feel the need to improve their living conditions | 40,5 | 18,2 | 41,5 | 29,0 | | not defined | 0,7 | 0,0 | 0,0 | 1,7 | Health and accessibility of medical services. In the analysis of this area, it is of particular concern that the main problems for the rural population here are not only financial constraints, but also territorial accessibility of social services. When assessing, rural families with children pointed to the problems of great remoteness of facilities for physical education and sports (57%), pharmacies (52.6%), accessibility of medical services (37.3%) [11]. There is a paradoxical situation when even the services of commercial enterprises, such as pharmacies, are not readily available to the rural population.
It is noteworthy that in parents' estimates of the morbidity of children, the indicators characterizing it revealed significant differences between urban and rural children (table 2). In addition, of the total number of children who do not play sports due to the state of health established by doctors, urban children account for 11.3%, and rural children account for 3.5% compared to them [11]. Table 2 Assessment of the incidence of children under the age of 15 by their parents in 2022, % [11] | Evaluation criteria | All respondents | including residents | | in urban settlements | in rural settlements | | Total | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | | including morbidity during the examination period: | | I was not ill (with being on bed rest) | 56,4 | 43,8 | 78,3 | | I was sick (with being on bed rest) | 43,6 |
56,2 | 21,7 | In this regard, it is significant that according to the results of the survey, more than 24% of the families of respondents with children under 15 years of age indicated that if they need treatment for children, they will not be able to use the services of paid specialists. Education. Taking into account the relatively low income security of families with children, especially those with many children, collecting a child for school and providing him with everything necessary for this remains a serious problem (table 3). Table 3 Providing children under the age of 15 with everything necessary for school in 2022, % [11] | Evaluation criteria | All respondents | including residents | | in urban settlements | in rural settlements | | Total | 100,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | | including those living in households that can provide everything they need: | | | | |
Without difficulty | 45,4 | 42,4 | 50,1 | | somewhat difficult | 41,1 | 44,7 | 35,3 | | very difficult | 13,5 | 12,9 | 14,5 | However, it should be noted that in the region the current system of social support measures for large and low-income families includes payments of a cash allowance by September 1 for the purchase of school uniforms. This right is enjoyed by low-income families raising three or more children. The amount is determined depending on the actual expenses, but no more than 4,489 thousand rubles in 2023. In addition, first-graders from large families are given a set of school writing materials for free by September 1 [22]. It should be noted that this area – providing general education for children is practically the only one in which the effect of such a differentiating factor as living in rural areas is actually smoothed out. In particular, according to such an analyzed parameter as the use of information technologies in education, the trends in the urban/rural context are almost identical and there is practically no significant difference between rural and urban schoolchildren. Most families, regardless of their place of residence, provide children with access to information technology in the learning process. However, the directions of children's development listed below are characterized by opposite trends and cannot always be provided by families, since they involve additional financial costs. Opportunities for full and comprehensive development. Among households with children, a relatively high proportion of those who indicated that economic reasons are a serious obstacle to ensuring full-fledged development, namely the involvement of children in paid activities, attending additional classes, the difficulty of buying the necessary equipment for sports and visiting sections. It should also be noted that the situation is worse in almost all positions of rural children, compared with urban children, as evidenced by the survey results shown in table 4. Table 4 Lack of conditions for the full development of children under the age of 15 in 2022, % [11]
| Evaluation criteria | All respondents | including residents | | in urban settlements | in rural settlements | | they pointed out the lack of conditions for the full development of children due to the absence of: | | opportunities to attend additional classes to develop their abilities on a paid basis | 41,3 | 37,3 | 49,4 | | opportunities to leave home for the holidays for at least 1 week | 36,8 | 34,1 | 42,2 | | opportunities to participate in school events that are paid | 23,7 | 21,3 | 28,3 |
| equipment for outdoor activities (bicycle, roller skates, etc.) | 19,5 | 21,9 | 14,7 | | the ability to change clothes and shoes in a timely manner as you grow | 3,4 | 4,0 | 2,1 | | A suitable place to play, study, or do homework | 5,8 | 5,7 | 5,9 | The opportunity for children to attend cultural and entertainment events is a very important indicator of the quality of life. At the same time, as the survey results showed, 11.5% of urban and 26.6% of rural households with children aged 3-14 years do not have sufficient income to attend cultural and entertainment events at least once a month [11]. Sports are also an important area of health promotion and comprehensive development of children. As the data showed, on average, up to half of the children in families are involved in sports and active games. However, in cities, the percentage of such is on average higher than in rural areas – 60.8% versus 48%. However, only 30% of children attend sports clubs on a regular basis [11]. As the data show, one of the main reasons preventing sports is a lack of desire. Almost half of the respondents indicated this reason. Other hindering reasons are diametrically opposed. For urban families, this is a high payment, and for rural families, the dominant reason was the lack of nearby places for sports. The analysis showed that today, for almost half of families with children in the region, their socio-economic status acts more as a factor limiting their opportunities. In addition, factors of differentiation of families with children in terms of the level and quality of life in the region are large families and living in rural areas. Compensating factors. Assessing the socio-economic situation of families with children is an important aspect of their research. However, the family's resource capabilities are not limited only to its income and financial situation. Within the framework of domestic research, significant material has been accumulated regarding the influence of various components of family capital on the implementation of youth life plans, which can be generalized in the region regarding modern practices of families with children [2; 4; 8].
One of the most important theoretical and methodological provisions of modern Russian sociology is the conclusion that the financial situation of families does not play an unambiguous determining role in the formation of the younger generation. "The influence of the family becomes an effective factor in the realization of the life trajectories of young people if it contains resources of different origins – economic, cultural, spiritual, symbolic" [2]. The data accumulated in domestic studies show that, according to the younger generation, among the factors that play the most significant role in achieving life goals and needs, the components of cultural, human and social capital of the family are in the leading positions – the value and semantic orientations of parents, the microclimate and parenting style in the family, the social ties of parents (total weight – 83 %). Indicators such as income and property of parents, successful marriage of children, complete the rating of the importance of components of the family's resource capital for the formation of youth success (26%). Financial resources are more influential in the families of owners, high-status employees (43%), as well as in families with one child [2]. These results confirm the general trend for modern Russian reality, according to which "...economic capital does not play a leading role in the social mobility of young people, it acts indirectly through other cultural and human components" [2]. According to the above research, social optimism, mutual assistance and support in the family, friendly and status ties of the older generation, high working capacity, family and kindred traditions are the basic components on which the majority of Russian youth plans to build their future life path. And this, in turn, leads to another main conclusion that, taking into account the conversion property inherent in family capital, in conditions of the formation of an insufficient level of financial capital of families with children, it is necessary to compensate it at the expense of human and cultural resources, including social capital, including a system of social ties. From the perspective of the theory of family capital, the family can be considered as the main source of social capital, which is realized in obligations, relationships of trust and assistance to each other, is, along with financial and cultural capital, a productive resource, and has an appropriative character, "... contributes to the achievement of certain goals, which cannot be achieved in its absence" [5; 7 23]. A.T. Konkov, taking into account the property of converting forms of family capital, in this regard notes: "... Social ties, obligations, trust, can ensure the receipt of financial and material capital, can be used to improve the quality of human capital ..." [23]. Social capital is a guide for children to the resources of social connections and the human capital of adult family members. The measure of the social capital of a family available to children is determined by the degree of relations between its members and depends on: the physical presence in the family and the level of attention paid by adult family members to the child; the size, quality and degree of range of social ties of family members; expectations of reciprocity; willingness of parents to invest in the development of the younger generation. A household survey in the Republic of Belarus showed that 77.6% of parents are focused on continuing their child's education, while every second wants to give him a higher education [11]. However, the low income level of parents may make it difficult to form a high level of children's human capital due to the fact that it will limit access to paid additional services for preparing for university admission: tutoring services, additional courses, learning foreign languages, buying necessary literature, etc. Thus, a low level of financial capital, measured by low income families can restrict access to higher education and prevent admission to public places. What should I do in this case? Let's consider below the mechanism of social capital, which makes it possible to compensate for the lack of financial capital. Based on the theory of J. According to Coleman, it is precisely this intra–family resource - social capital, that actively influences, and in some cases is decisive in achieving and choosing the direction of professional education for the younger generation. J. Coleman, one of the first to define the "family background" and highlight financial, human and social capital in it, indicated that social capital (the relationship between older family members and children) is the main family social resource that affects the development of human capital and educational achievements of students. However, J. Coleman himself noticed the following correlation: the more children there are in a family, the more this attention to education becomes "diluted". Studies on the accessibility of higher education in Russia show that the human and social capital of a family is more significant and affects the choice and admission of children to vocational educational institutions than the learning process in them [4; 10]. They create a cognitive environment, helping to obtain the necessary knowledge for admission, form a common cultural level, set directions in professional self-determination, form behavioral models and form an assessment of children's own prospects in this field. In addition, modern domestic research shows that different Russian families have different levels of willingness to invest in the education of their members. It is a well-known fact that parents' income and educational level have a strong influence on educational strategies. However, an important and often decisive criterion here will be the level of the family's social capital. An analysis of research on this issue shows that if the level of social capital of a family is high, then it is ready to go to the costs associated with obtaining the desired level of education for their child, regardless of the level of financial capital of the family (low or high incomes). A higher level of family social capital will increase the willingness to invest in children's education by 2 times. At the same time, parents will consider not only the possibilities of their income, but also loans, as well as the inclusion of their social ties in order to obtain cash loans from friends and relatives to pay for university tuition (this thesis is convincingly confirmed by research on similar issues) [9]. Thus, the compensatory mechanism of the social capital of the family consists in the fact that it can mobilize the financial capital of the family to solve important consumer family tasks and partially replace the deficit of financial and human capital. Conclusion
The conducted research has shown that financial capital for a significant part of families with children acts rather as a factor limiting development opportunities and access to social benefits and services. The risk of reducing opportunities for the full and comprehensive development of children in families in the region is caused primarily by their low income and factors such as having many children and living in rural areas. At the same time, the social capital of families can act as a compensating factor and even expand life opportunities, in particular in the field of education.
References
1. Putin, V.V. (2023). “Talk about important things” Retrieved from http://www.kremlin.ru/events/president/news/72171
2. Shinyaeva, O.V., & Ushkova, Yu.V. (2018). Family capital and its dependence on the social characteristics of families. News of higher educational institutions. Volga region. Social Sciences, 1(45), 120-133.
3. Shkaratan, O.I., & Yastrebov, G.A. (2010). Sociocultural continuity in the Russian family: (experience of empirical research). Social sciences and modernity, 1, 5-27.
4. Fursova V.V., & Ha Van Hoang. (2016). The influence of the family’s sociocultural capital on the accessibility of higher education (on the example of Russia and Vietnam). Sociology and society: social inequality and social justice: materials of the V All-Russian Sociological Congress, pp. 979-985. Moscow: Russian Society of Sociologists.
5. Bourdieu, P. (2007). Sociology of social space. Transl. from French; resp. ed. translation by N.A. Shmatko. M.: Institute of Experimental Sociology; St. Petersburg: Aletheya.
6. Radaev, V.V. (2003). The concept of capital, forms of capital and their conversion. Social sciences and modernity, 2, 5-16.
7. Coleman J. Social and human capital. Retrieved from https://psycho.ru/library/3930?ysclid=lo0jq2sg2d652743983
8. Roshchina, Ya.M. (2012). Family capital as a factor in the educational opportunities of Russian schoolchildren. Educational Issues, 1, 257-277.
9. Sysoev, S.A. (2010). Intrafamily social capital as an incentive for investment in human capital. Journal of economic regulation (Issues of economic regulation), 1(4), 42-64.
10. Yuzhakova, E. V. (2019). The relationship between family and social capital: theoretical and methodological analysis. Strategies for the development of social communities, institutions and territories: materials of the V International Scientific and Practical Conference, Yekaterinburg, April 22-23, 2019: in 2 t. Ekaterinburg: Ural Publishing House. Univ., T. 1. P. 170-175. Retrieved from http://hdl.handle.net/10995/77077
11. Materials of the Territorial Body of the Federal State Statistics Service for the Republic of Bashkortostan. Bashkortostanstat. Retrieved from https://02.rosstat.gov.ru
12. Ayvazyan, S.A., & Isakin, M.A. (2006). Integral indicators of the quality of life of the population of the region as criteria for the effectiveness of socio-economic policy pursued by government authorities. Applied econometrics, 1, 25-31.
13. Venediktova, S.G. (2010). Model of a quality of life management system. Standardization in managing the quality of life of the population in the region: abstract. ...cand. econ. Sci. St. Petersburg.
14. Colin, K.K. (2020). Quality of life in the strategy of ensuring national and global security // Design of the future. Problems of digital reality: proceedings of the 3rd International Conference (February 6-7, 2020, Moscow). M.: IPM im. M.V. Keldysh, pp. 91-102. Retrieved from https://keldysh.ru/future/2020/8.pdf https://doi.org/10.20948/future-2020-8
15. Korchagina, I.I., Prokofieva, L.M., & Ter-Akopov, S.A. (2019). Material deprivation in poverty estimates. Population, 2, 51-63.
16. Methodological recommendations for the implementation of target models of the National Social Initiative (NSI) in the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Retrieved from https://src-sakha.ru/medias/docs/asi_nsi/ %D0%A3_174%2015-06-2021_%D0%9C%D0%B5%D1%82%D0%BE%D0%B4-% 20%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BC%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B4%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D0%B8. pdf
17. RIA Rating. Rating of Russian regions by quality of life – 2022. Retrieved from www.riarating.ru.
18. Rossoshansky A.I., & Chekmareva E.A. (2016). The structure of the quality of life of the population in Russian and foreign studies. Social space, 1(3). Retrieved from http://www.volnc.ru/files/journal/issues/sa-2016-1-3-22fc349da5-struktura-kacestva-zizni-ru.pdf
19. Zakharova, S.G. (Ed). (2019). Managing the quality of life of the population: monograph. Nizhny Novgorod: Research Center “Open Knowledge”.
20. Svinukhova, Yu.N. (2018). The main factors in the formation of social tension and the growth of conflict potential in modern Russia and its regions (on the example of the Volga Federal District). National Security / notabene, 6, 1-11. Retrieved from https://nbpublish.com/library_read_article.php?id=28411. doi:10.7256/2454-0668.2018.6.28411.
21. Sukneva, S.A., Barashkova, A.S., & Postnikova, K.Yu. (2020). Fertility, children and family income: trends and relationships. Economic and social changes: facts, trends, forecast, 13(2), 201-213.
22. Payments before school for children in Ufa. Retrieved from https://mkset.ru/news/2023-07-05/vyplaty-pered-shkoloy-na-detey-v-ufe-2975653.
23. Konkov, A.T. (2006). Social capital as a concept of economic sociology and its role in the system of economic interaction. Author's abstract. dis. ... Doctor of Social Sciences. Moscow. Retrieved from https://textarchive.ru/c-2854336-pall.html
Peer Review
Peer reviewers' evaluations remain confidential and are not disclosed to the public. Only external reviews, authorized for publication by the article's author(s), are made public. Typically, these final reviews are conducted after the manuscript's revision. Adhering to our double-blind review policy, the reviewer's identity is kept confidential.
The list of publisher reviewers can be found here.
The subject of the research in the presented article is the resource capital of the modern family in the Republic of Bashkortostan, taking into account the differentiation of opportunities and compensating factors. As the methodology of the subject area of research, theoretical methods were used in this article, including the descriptive method; the method of categorization; the method of analysis, as well as a resource approach, statistical data analysis, secondary analysis of sociological research data on related issues. The relevance of the article is beyond doubt, since against the background of the tense geopolitical situation in such a difficult period for Russia, more and more attention is being paid to the development of the family as a powerful framework for the progress of Russian society and a stronghold of traditional values. The question of the role of the parental family, the importance of family resources and the possibilities of using their entire arsenal in the implementation of the life strategies of the younger generation can be considered classic in sociological science. However, from the point of view of quality of life management in the regions, the relevance of the study is determined by the need to monitor and assess the needs and access to social benefits and services of families and their members, which will determine some mechanisms for improving their socio-economic status, respectively, well–being and quality of life, and will also determine the characteristics and degree of influence of various the types of her capital in family education. In addition, it was noted that this study was carried out within the framework of the state task of the UFIC RAS No. 075-01134-23-00 for 2023 and for the planning period of 2024 and 2025. The scientific novelty of the study consists in analyzing various models and methods of managing the quality of life of families with children in the Republic of Bashkortostan, taking into account 5 main components: income assessment; assessment of the level of housing and household provision; assessment of the level of accessibility of medical services; assessment of accessibility of education and additional services in this area; assessment of opportunities for full-fledged development. The article is presented in the language of scientific style with a very competent use in the text of the study of the presentation of the positions of a number of scientists on the current problem under study, as well as the use of scientific terminology on the topic of research. The structure is designed taking into account the basic requirements for writing scientific articles. The structure of this study includes an introduction, methods, results, conclusion and bibliography. The content of the article reflects its structure. In particular, the article provides tables and a drawing that clearly reflect the results of the study. Especially valuable in the content of the study is the consideration of the compensatory mechanism of the family's social capital, which consists in the fact that it can mobilize the financial capital of the family to solve important consumer family tasks and partially replace the deficit of financial and human capital. The bibliography contains 23 sources, including domestic periodicals and non-periodicals, as well as electronic resources and official websites. The article describes various positions and points of view of different scientists characterizing various aspects of quality of life, well-being, household development, social capital, social relations in the family, including between different generations, and also contains an appeal to various scientific works and sources devoted to this topic, which is included in the circle of scientific interests of researchers, dealing with the specified problem. The presented study contains the main conclusions concerning the subject area of the study. In particular, the study showed that financial capital for a significant part of families with children acts more as a factor limiting development opportunities and access to social benefits and services. The risk of reducing opportunities for the full and comprehensive development of children in families in the region is caused primarily by their low income and factors such as having many children and living in rural areas. At the same time, the social capital of families can act as a compensating factor and even expand life opportunities, in particular in the field of education. The materials of this study are intended for a wide range of readers, they can be interesting and used by scientists for scientific purposes, teaching staff in the educational process, government and municipal employees, analysts, representatives of public organizations dealing with family and children issues. As a recommendation, the authors should pay attention to the need to design a bibliography in accordance with the requirements of the current GOST of bibliographic descriptions. This is especially true for the design of sources representing official websites and electronic resources indicated in the bibliography, in particular, there is no date of reference when they are designed. If possible, the list of bibliographic sources should be shortened for the publication of the article. These recommendations do not reduce the high scientific significance of the study itself, but rather relate to the design of the text of the article. It is recommended to publish the article.
Link to this article
You can simply select and copy link from below text field.
|
|





